Strep Throat
January 10, 2020
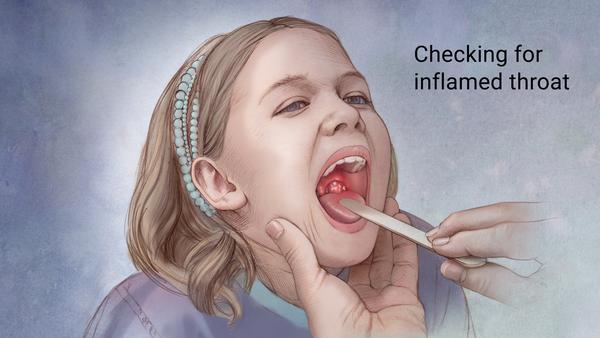
Group A streptococci is a bacterial infection that usually presents in children age 3 and over.
An infected child will typically become ill 2 to 5 days after being exposed to streptococcal bacteria. Group A streptococcal infections are very contagious. Throat infections, for example, are passed through the air by sneezing, coughing, or touching an infected child.
Signs of strep include:
sore throat, fever, headache, gastrointestinal upset, rash, white patches of pus on the tonsils, swollen glands in the head and neck, and/or cold symptoms.
When to Call Your Pediatrician
If your child has a sore throat, especially with pus on the tonsils or swollen glands, and/or fever contact your pediatrician.
How Is the Diagnosis Made?
Your doctor will swab your child’s throat and tonsils to test whether he has a strep infection. Some pediatricians’ offices have quick-result streptococcal tests that can help diagnose streptococcal infection in several minutes.
Treatment
The primary treatment for strep sore throats is an antibiotic given orally or through an injection. When antibiotics are given to treat a Group A strep infection, your child should recover fully. However, if his throat infection goes untreated, the infection may spread to other parts of the body. He can develop an ear or sinus infection. Group A streptococcus can also lead to rheumatic fever, a rare disease affecting the heart and joints, or glomerulonephritis, a kidney problem in which urine turns a brownish color and blood pressure increases.
Children with strep infection should not return to school or child care until they’ve been taking antibiotic treatment for at least 24 hours and they are fever free for at least 24 hours without fever medication.
For any questions please contact your child’s pediatrician to discuss in detail.
Photo courtesy of google images
Next Post >>